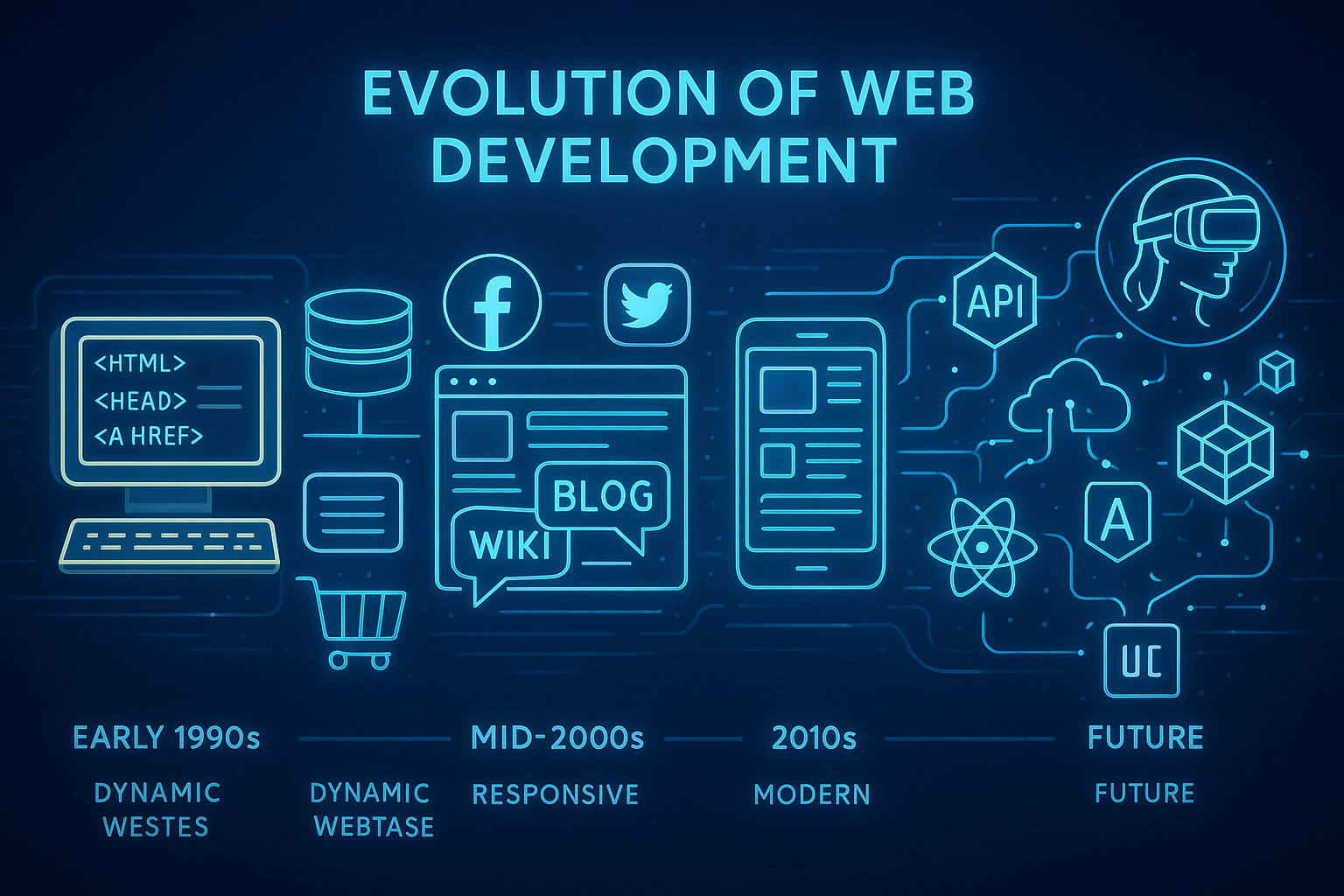
The Early Days of Web Development – Static
Web development came about in the early 1990s with static web pages containing nothing but some simplistic (but very effective and persuasive) HTML code (Hyper Text Markup Language). Static websites had text; hyperlinks; limited design capabilities; but back then, web developers did not have sophisticated tools or frameworks, and mostly coded by writing one line at a time. There were very limited capabilities for developers. No forms, no databases, not even animation. Web browsers such as Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer were just starting to gain popularity. Ultimately the goal of the website was information. When businesses began to use static pages, they were basically online brochures with almost no interaction.
Search engines as well were very limited tools at best, and did not have the advanced technology of today's robots. It took time (and trial and error) to find even a relevant page of content. However, this time period laid the groundwork for modern web development. Early static sites established the value of an online presence. Even still, the static era established the importance of SEO techniques-- use of post headings, meta tags, layout, etc. So while static sites may seem primal and unnecessary with hindsight, they ushered in a future that would become diverse, enormous, and complex.
The Era of Dynamic Websites and Server-Side Scripting
As individuals and businesses became more comfortable with the internet in the late 90’s and early 2000’s, they began to demand more interesting or interactive websites. This advancement in the web development world brought about dynamic web development, utilizing server-side scripting languages such as PHP, ASP, and frameworks like Django or Ruby on Rails. Dynamic websites could soon pull information directly from MySQL or PostgreSQL database allowing dynamic (or interactive) content to change depending on user inputs. E-commerce platforms could now set-up product catalogs, shopping cart workflows and secure checkouts.
This advancement truly paved the way for a complete shift in web development trends. Web applications became much more interactive such as the ability to comment on posts, create blogs, and present them in CMS. Websites like Amazon, eBay, and early social websites were getting positive traction by offering tailored content and results. Developers began to explore design considerations like how to scale their applications, or how to manage users securely.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) also began to change at this time. Rather than just keyword stuffing, websites needed to identify a method to deliver new content that was interesting and/or designed for their users to rank higher in the search engines. Dynamic websites provided a way to adopt quick modification/routines, which ultimately helped improve search engines, SEO, and user engagement in general. This is where the interactive web truly became relevant enough to create the future innovations we are familiar with today.
Web 2.0 and the Social Media Revolution
In the middle of the 2000s, the Internet transitioned from information-based websites to user-centered and interactive websites known as Web 2.0. Developers were able to utilize communication technologies like AJAX, JavaScript, and CSS to create seamlessly dynamic user experiences. This period in the digital world gave birth to existing internet giants like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter, transforming user-to-user interactions like never before in the 21st century.
This development resulted in a new notion of web-based interactivity, which moved from static content consumption to collaborative experiences that engaged internet users. User-generated content, blogs, wikis, and forums defined this evolution. New, enriched content features like live commenting, instant messaging, and video streaming were fast to enter the mainstream. Existing and new tools for front-end development enhanced the development experience, allowing developers to build beautiful, responsive, and mobile-first designs that adjusted to screen sizes.
From an SEO perspective, the Web 2.0 movement defined signals of content quality (high-quality content), backlink signals to websites (backlinks), and signals of user engagement metrics to website visibility (user engagement metrics). Additionally, social media became an early driver of the user traffic experience and brand visibility across the internet. (McKenzie, 2022). A keen awareness developed among smaller firms that Building a digital presence as critical to their growth strategy. There was no longer a question of whether a digital presence was needed, but how to grow it. The growth of Web 2.0 truly democratized the internet and empowered developers, organizations, and users to create and share content across a networked information system.
The Mobile-First Age and Responsive Design
As the years rolled on through the early 2010's we just witnessed an explosion of smart phones and tablets. This transformation introduced a whole set of new challenges for web developers... namely, how websites can look and work across multiple devices, regardless of screen size. This was where the notion of responsive web design came in, allowing website layouts to simply adjust the layout based on the device the user is using. Coupled with frameworks like Bootstrap and Foundation, building a mobile site was no longer thinning about the layout as a responsive website made for a cleaner mobile friendly website without the need to "shrink" things down.
The mobile-first approach quickly became a leading, trending way for web developers to think, and not long after, Google's ranking algorithm was updated to reflect how a website was optimized for mobile. This meant that if a business wanted to have higher ranking in serps, they could no longer ignore how WhatsApp performed or operated on smaller devices.
During this time, progressive web apps were also introduced, supporting the best of both worlds of websites and mobile apps, allowing offline support capabilities, fast load times, and push notification and sharing strategies.The front-end technology stack of HTML5, CSS3 and JavaScript frameworks (Angular, React, Vue) allowed developers to build complicated applications that worked in the browser in the same way traditional web applications had worked.
From an SEO perspective, page speed, mobile usability and user experience / UX monetized in being the most important ranking factors. The mobile-first revolution came along and changed how we designed, developed and optimized websites for users and search engines alike.
Modern Web Development - APIs, Cloud and Frameworks
Today’s web development is mainly characterized by frameworks, cloud, and API architectures. Instead of building things from the bottom up, developers build on libraries and frameworks such as ReactJS, Angular, Vue.js, Laravel, and Node.js. These widely adopted frameworks enable creators to build scalable, modular, and extremely performant web applications.
APIs (application programming interfaces) have become the gold standard in modern web development and are needed for nearly every platform, service, and application Kubernetes architecture. For example, APIs greatly simplified how payment gateways like Stripe or PayPal are integrated into your application. APIs also allow for connecting with Google Maps and other social media platforms.
Cloud technology revolutionized how hosting and scaling works. AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure play a critical role in enabling websites and applications to manage millions of users while maintaining minimal downtime using serverless or distributed systems.
From an SEO perspective, today's development practices need to ensure that their application is equipped with structured data, schema markup, Core Web Vitals, and technical SEO, among others, in order to rank better. Additionally, modern developers continue to focus on important aspects, such as application performance, bounce rate, and securing their user's data with HTTPS and more advanced encryption.
The Future of Web Development – AI, Web3, and Beyond
Looking to the future, web development is advancing faster than ever before. Technology is evolving away from the static web pages in HTML and CSS to web applications that are built with new technologies - AI, ML, Web3, blockchain, etc. This represents developers moving into a future of smarter websites, where data is housed, data is analyzed, and the whole experience is driven by the visitor's behavior. AI-driven platforms can now be utilized to create personalization and provide automated tools, such as Generative AI attempts to code a website for you. This is tremendous progress from a static web page.
Web3, and decentralized applications (dApps) will redefine applications toward user ownership of data, increasing secure transactions, and using blockchain to authenticate your identity. The prevalence of cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and smart contracts will most certainly impact how we use online platforms.
The future of web development, combined with the development of 5G technology will create advanced web performance for content consumption, streaming, real-time communication, and immersive technology like Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR). Developers like many of you will search for advanced methods for organizations to create engaging, secure, and accessible websites in the future.
If your website relies on consumers finding your content, the future web development will create huge challenges for SEO, voice search optimization, AI-triggered ranking algorithms, and semantic search. Organizations wishing to compete must continuously evolve how they are viewed in the online space.